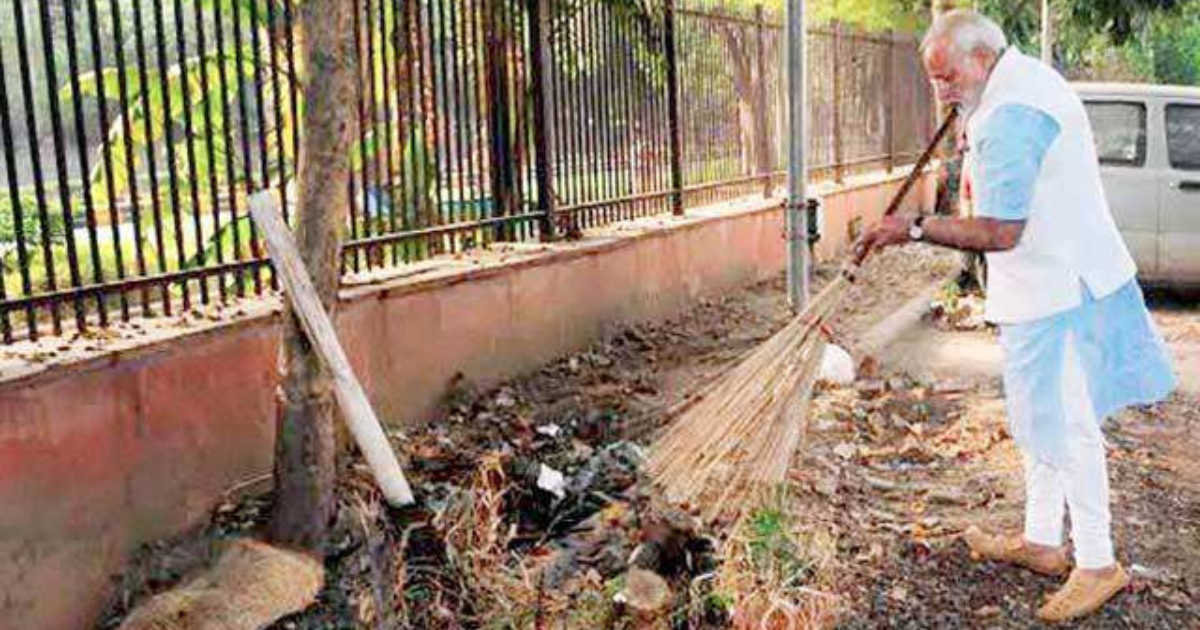
Sanitation is a fundamental necessity for a healthy and dignified life. However, for decades, India faced severe challenges in maintaining cleanliness, managing waste, and providing access to proper sanitation facilities. To address this issue, the Swachh Bharat Yojana (SBY), also known as the Swachh Bharat Abhiyan (SBA), was launched by the Government of India on October 2, 2014. This nationwide campaign aims to achieve a clean and open-defecation-free (ODF) India by improving sanitation infrastructure and promoting hygiene awareness.
Swachh Bharat Yojana has brought significant changes in urban and rural sanitation, waste management, and overall public health. This article explores how the initiative is transforming sanitation in India, its impact, challenges, and future prospects.
Objectives of Swachh Bharat Yojana
The key objectives of Swachh Bharat Yojana include:
- Eliminating open defecation and ensuring proper toilet access for all households.
- Promoting hygiene awareness and behavior change at the community level.
- Encouraging waste management and recycling practices.
- Developing sustainable sanitation infrastructure in urban and rural areas.
- Engaging citizens, NGOs, and private organizations in cleanliness drives.
Key Components of Swachh Bharat Yojana
1. Swachh Bharat Mission – Urban (SBM-U)
This initiative focuses on sanitation challenges in urban areas and includes:
- Construction of household, community, and public toilets.
- Implementation of solid waste management systems.
- Awareness campaigns to encourage hygiene practices.
- Involvement of municipal bodies for better waste collection and disposal.
2. Swachh Bharat Mission – Rural (SBM-G)
The rural segment of the mission aims to provide sanitation facilities in villages by:
- Constructing toilets for every rural household.
- Encouraging the use of bio-toilets and eco-friendly practices.
- Promoting behavioral change through education and local engagement.
- Ensuring proper waste disposal and treatment systems.
Impact of Swachh Bharat Yojana on Sanitation
1. Open Defecation Free (ODF) India
One of the most significant achievements of Swachh Bharat Yojana has been the reduction in open defecation. According to government reports:
- Over 100 million toilets have been built across India.
- More than 600,000 villages have been declared ODF.
- Cases of diarrhea and waterborne diseases have reduced due to improved sanitation.
2. Improvement in Waste Management

Waste disposal and management have seen a considerable transformation:
- Segregation of dry and wet waste has been encouraged.
- Municipal bodies have adopted door-to-door garbage collection services.
- Recycling and composting initiatives have gained momentum in many cities.
3. Women Empowerment and Dignity
SBY has played a crucial role in empowering women by ensuring toilet accessibility:
- Women no longer have to travel long distances for sanitation needs.
- The risk of harassment and assault has significantly reduced.
- Schoolgirls have better access to hygienic toilets, improving attendance rates.
4. Behavioral Changes and Hygiene Awareness
The mission has successfully instilled cleanliness habits among people through:
- Mass awareness campaigns involving celebrities, influencers, and community leaders.
- Swachh Bharat volunteers and NGOs conducting cleanliness drives.
- Schools incorporating sanitation education in their curriculum.
5. Economic and Environmental Benefits
- Improved public health has reduced healthcare costs related to sanitation-related diseases.
- Clean surroundings have boosted tourism and local businesses.
- Waste-to-energy plants and composting have led to sustainable waste management.
Challenges in Implementing Swachh Bharat Yojana
Despite its success, the initiative faces some challenges:
1. Sustaining Toilet Usage
While millions of toilets have been built, ensuring consistent usage and maintenance remains a challenge in some areas.
2. Waste Management Issues
- Many cities still lack proper waste segregation and disposal facilities.
- Plastic pollution and untreated sewage remain major environmental concerns.
3. Behavioral Resistance
Some communities, particularly in rural areas, continue to practice open defecation due to deep-rooted traditions and lack of awareness.
4. Infrastructure and Financial Constraints
- Many local bodies struggle with funds to maintain sanitation facilities.
- In some areas, poor water supply affects the usability of toilets.
Government Measures to Overcome Challenges
To address these challenges, the government has:
- Launched the ODF+ and ODF++ frameworks to ensure the sustainability of sanitation efforts.
- Introduced the Swachh Survekshan ranking system, motivating cities to improve cleanliness.
- Strengthened solid waste management policies with a focus on recycling and plastic waste reduction.
- Partnered with private organizations to fund sanitation projects.
Success Stories of Swachh Bharat Yojana
1. Indore – India’s Cleanest City
Indore has ranked as India’s cleanest city for several years due to its:
- Efficient waste segregation and recycling programs.
- Well-managed door-to-door garbage collection.
- Active citizen participation in cleanliness campaigns.
2. Rural Sanitation Success in Uttar Pradesh
Many villages in Uttar Pradesh have become completely open defecation-free due to government incentives and local participation.
Also Read: PM Awas Yojana: Transforming Housing Dreams Into Reality
Conclusion
Swachh Bharat Yojana has revolutionized sanitation and cleanliness in India, making it a cleaner and healthier nation. By eliminating open defecation, improving waste management, and promoting hygiene awareness, the initiative has positively impacted public health and the environment. However, sustained efforts, community involvement, and technological advancements are essential to ensure long-term success.
FAQs
1. What is the main objective of Swachh Bharat Yojana?
The main objective is to achieve a clean and open-defecation-free India by improving sanitation infrastructure and promoting hygiene awareness.
2. How has Swachh Bharat Yojana impacted public health?
It has significantly reduced cases of diarrhea, cholera, and waterborne diseases by improving sanitation facilities.
3. What is the difference between Swachh Bharat Mission – Urban and Rural?
- SBM-U focuses on urban areas, building community toilets and waste management systems.
- SBM-G targets rural sanitation by constructing household toilets and promoting behavior change.
4. How can individuals contribute to Swachh Bharat Yojana?
People can participate by:
- Keeping their surroundings clean.
- Practicing waste segregation.
- Avoiding plastic waste.
- Educating others about sanitation and hygiene.
5. What is the ODF+ and ODF++ framework?
- ODF+ ensures that toilets are used and maintained properly.
- ODF++ focuses on treating liquid and solid waste effectively.

